Oh guys, welcome back! My name is Pavan, and this is the sixth chapter in our fundamentals course. This time, we will be talking about cloud deployment models and their key differences. Stay tuned! In our previous episode, we learned about service type models. This time, we will be learning about the deployment models.
Azure Course Chapter 5: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS cloud service models
Azure Course Chapter 4 : Consumption-based Model
Overview of Cloud Deployment Models

This section of the exam will test you on whether you know what a public, private, and hybrid cloud is, and what their differences are. Let me start with a public cloud.
Public Cloud
In order to understand the public cloud, we need to make a very clear separation of where we are deploying our services. We are either deploying them to the cloud service provider or inside of our own data center. When it comes to the public cloud, that means all our resources are hosted in a public cloud. That means we don’t own our own hardware anywhere.
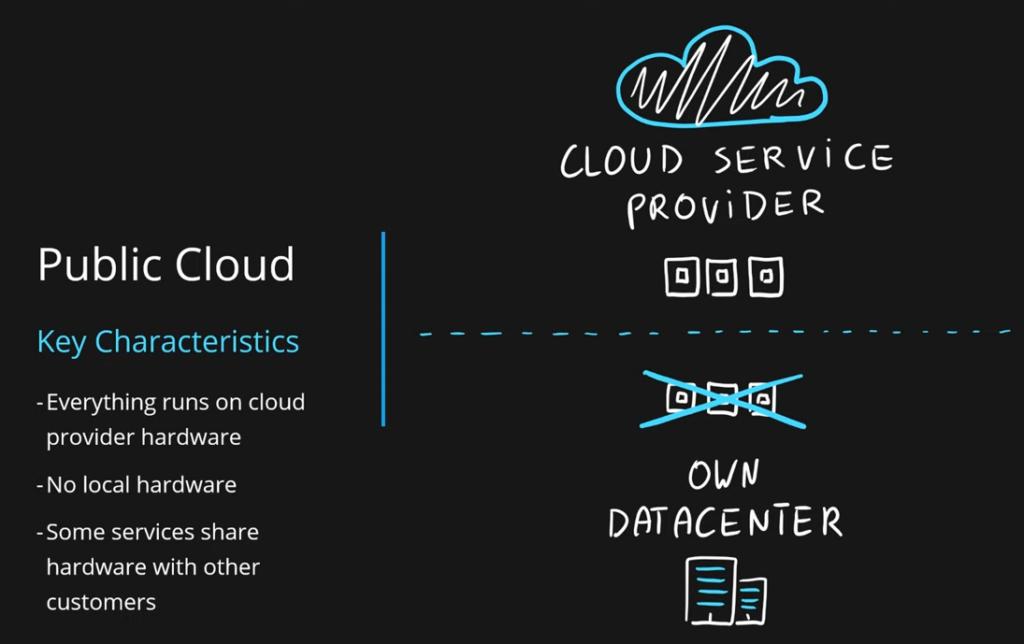
One thing to note is that in the public cloud, some services share the hardware with other customers. This is usually solved by just picking the right pricing tier, but you should be aware of that when you’re starting with the cloud and you have some security compliance policies in place. The public cloud is very simple to understand. In general, you’re hosting everything in the public cloud.
Advantages of Public Cloud
As with any deployment model, there are always advantages and disadvantages. In this case, when it comes to advantages, there’s no CapEx (capital expenditure). That means no big initial investment on your side, with the cloud being highly available and a drive by default to get those advantages by just simply going to the cloud.

Thanks to pay-as-you-go pricing and the consumption model we’re talking about, you only pay for the resources that you use. And because Microsoft manages all of the hardware, there’s no hardware maintenance required and, as such, no deep technical skills required from your teams.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
While there are some disadvantages, there is one major one when it comes to security and compliance as well. Cloud is secure by default, but there may be specific security requirements, government policies, industry standards, or legal requirements that the public cloud cannot meet. In that case, the public cloud might not be the right choice for you. There’s always an issue with ownership because if you want to maintain your own hardware or make changes to the hardware, then again, you cannot do that because Microsoft is hosting and managing all the hardware in their own data centers. If you have some specific unique business requirements, then again, the public cloud might not be the one for you.
Private Cloud
On the other hand, we have a private cloud, which is the reverse model. You don’t have anything in the public cloud; you host everything in your own data center. In this case, remember that you need to provide self-service in order to be actually considered a cloud, and you need to provide all the benefits of the cloud, except in your own data center. In this scenario, you are the one maintaining all the hardware.

Advantages of Private Cloud
So, let’s talk about the advantages and disadvantages of using a private cloud. The advantages are pretty obvious. Because you maintain everything, you have all the possibilities, so you can support pretty much any scenario. You have total control over the security, and as such, you can meet any security and compliance requirements.

Disadvantages of Private Cloud
But maintaining your own hardware comes at a cost, and that cost is a big initial capital expenditure investment that you need to make. There’s limited agility because that agility is limited by the amount of hardware and skills of your team. So, excellent skills and expertise of your internal team are pretty much mandatory when running a private cloud. And as you can imagine, this comes at a cost.
Hybrid Cloud
Which brings us to the third model, which is the hybrid model. In this model, you take advantage of both public and private cloud. You connect them together to provide the greatest flexibility out of these three options.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
So, when talking about the advantages and disadvantages, the obvious one is the great flexibility. But beyond that, you can run legacy applications in your private cloud, utilize existing infrastructure, meet any security requirements, but for everything else, move to the cloud and take advantage of all the good stuff from the cloud.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
In this case, the disadvantages are pretty obvious. A bigger environment consisting of both public and private cloud might be more expensive, but is definitely more complicated to manage. And as such, it puts a bigger strain and bigger requirement on the skills and expertise of your internal IT teams.
Thats it for today, Please Check Previous chapters for revisions
